Creatine Monohydrate Powder
Your order will be shipped tomorrow
Benefits
Time to notice full effects: 3-4 Weeks
-
Metabolism
-
Physical Energy
-
Mental Energy
-
Muscle Mass
Summary
Creatine Monohydrate (200 Mesh) is a compound stored in muscles, known for enhancing metabolic health, boosting physical and mental energy, and increasing muscle mass and strength, making it ideal for improving overall performance.
Product Usage
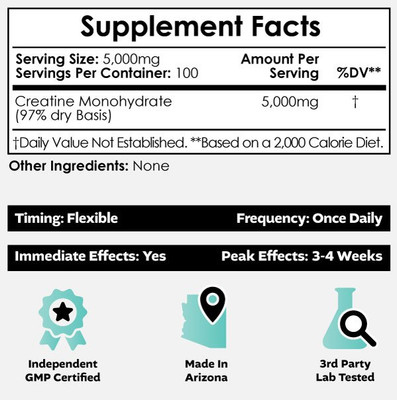
5g (Per Serving)
Flexible
With Or Without Food
1 Time Daily
The Science
Who Are They?
- Dr. Lindsey Faucette, DO, Board Certified
- Dr. Lance Dreher, (Doctor Fitness) PhD
- Dr. Francisco Chacon PhD
- Kerry Hughes, M.Sc., RH(AHG), FDN-P
What Our Scientific Board Does
The Process
What Do They Do?
- Review Product Claims
- Review Cited Research
- Suggest Changes to Claims
- Approves Final Conclusions
Overview Of The Scientific Evidence
Our Research Snapshot
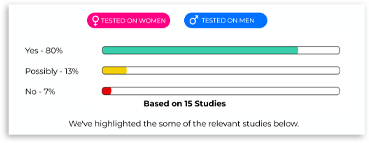
What Does The Research Show?
Available scientific research shows that creatine monohydrate reliably enhances high‑intensity exercise performance, muscle mass, and strength, with emerging evidence for benefits on cognitive function and overall energy metabolism
See The Scientific EvidenceBuild Your Stack
Unlock your full potential by building a supplement stack tailored to your unique goals. Whether you're focused on energy, focus, or overall wellness, we’re here to guide you in creating the perfect combination of supplements to support your journey. Your health, your way—powered by the right stack.
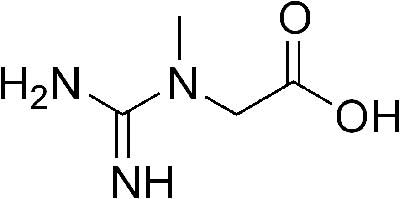
What is Creatine Monohydrate (200 Mesh)?
Creatine was first discovered in 1832 when Michel Eugène Chevreul isolated it from a water extract of skeletal muscle. Chevreul later named the nitrogenous organic acid after “Kreas” which is the Greek word for meat. While Creatine is primarily synthesized in the liver and kidneys via the amino acids glycine, arginine, and methionine, it is believed that 95% of the Creatine in our bodies is actually stored in our muscles. The remaining 5% is found in our brain, kidneys and liver. Creatine can also be obtained through the foods we eat such as meat and seafood.
Creatine Structure
While many myths and rumors surrounding Creatine have been perpetuated in the media and elsewhere, Creatine is actually one of the most widely researched dietary supplements available to buy. In fact, it is estimated that over 500 research studies have been conducted. Creatine supplements are popular with athletes and bodybuilders due to its well-documented belief to support muscle size and growth. However, early research is also now suggesting that Creatine may be a natural nootropic as well.
How Does Creatine Work?
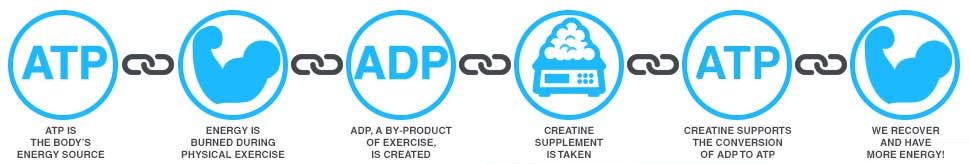
In short, Creatine helps supply energy to all cells in our bodies, especially muscle cells. Creatine does this by increasing the creation of ATP. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is considered vital to the process of sending energy directly to our muscles.
More specifically, Creatine plays a vital role in the phosphagen energy system which is responsible for synthesizing ATP in our bodies. While Creatine naturally occurs in our body as both free form Creatine and as Phosphocreatine, it is the Phosphocreatine that is believed to restore ATP (Adenosine triphosphate) in our muscles. When we workout, our stores of ATP are depleted due to the physical exertion. The general concept behind taking a Creatine supplement is that by having a surplus of Creatine in our muscles, it promotes the synthesis of ATP by converting it from ADP (adenosine diphosphate, a by-product of physical exercise). In turn, this promotes both mental and physical energy as well as recovery.
What are the Uses and Benefits of Creatine?
Uses and benefits of Creatine Monohydrate may include:
- Support a healthy metabolic rate*
- Support cognitive function*
- Promote physical and mental energy*
Creatine as a Natural Nootropic
- Creatine may support cognitive function*: One study demontrated that creatine monohydrate may help to increase mitochondrial health.
- Creatine may support memory and learning ability*: While young, healthy meat eaters may not yield the benefits of Creatine, at least one study has suggested that vegans and vegetarians may enjoy improved cognition, memory and learning ability by taking a Creatine supplement.
How to Use Creatine
As a dietary supplement, take 5000mg of Creatine Monohydrate (200 mesh) once daily.
When Should I Take Creatine?
Creatine beginners often ask whether it is better to take Creatine Monohyrate before or after a workout. While Creatine is generally thought of as a preworkout supplement, one recently published paper titled "The Effects of Pre Versus Post Workout Supplementation of Creatine Monohydrate on Body Composition and Strength” suggests that it may be better to take Creatine as a post workout supplement. All 19 participants that took Creatine Monohydrate as a post work out supplement noted improvements in comparison to taking Creatine before their workout. However, the same paper concluded that the benefits of taking Creatine after a work out instead of before were small by comparison.
While more research on this topic is needed, the current consensus remains that the best time to take Creatine isn’t as important as is the overall buildup of it in our bodies in order to enjoy the health benefits of Creatine Monohydrate.
Where Can I Buy Creatine?
Nootropics Depot offers 500g jars of high quality Creatine Monohydrate powder (200 mesh). Nootropics Depot's Creatine Monohydrate (200 mesh) has been lab-tested and verified for both product purity and identity.
To learn more, read the Creatine Monohydrate reviews and experiences below.
IUPAC: 2-[Carbamimidoyl(methyl)amino]acetic acid
CAS: 57-00-1
| *Attention: These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. |
Sources:
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Creatine
- https://examine.com/supplements/creatine/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23919405
- https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/10-benefits-of-creatine#section1
- https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/what-is-creatine#section1
Lab Testing Results / Certificate of Analysis (COA)
Trust Through Transparency
Your health matters, which is why we only use the best 3rd party ISO accredited labs and cGMP certified and FDA registered facilities right here in the USA
Learn more